Blood pressure is more than a routine doctor’s check—it’s a crucial measure of heart health. Understanding how it changes with age helps protect against heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
Why It Matters
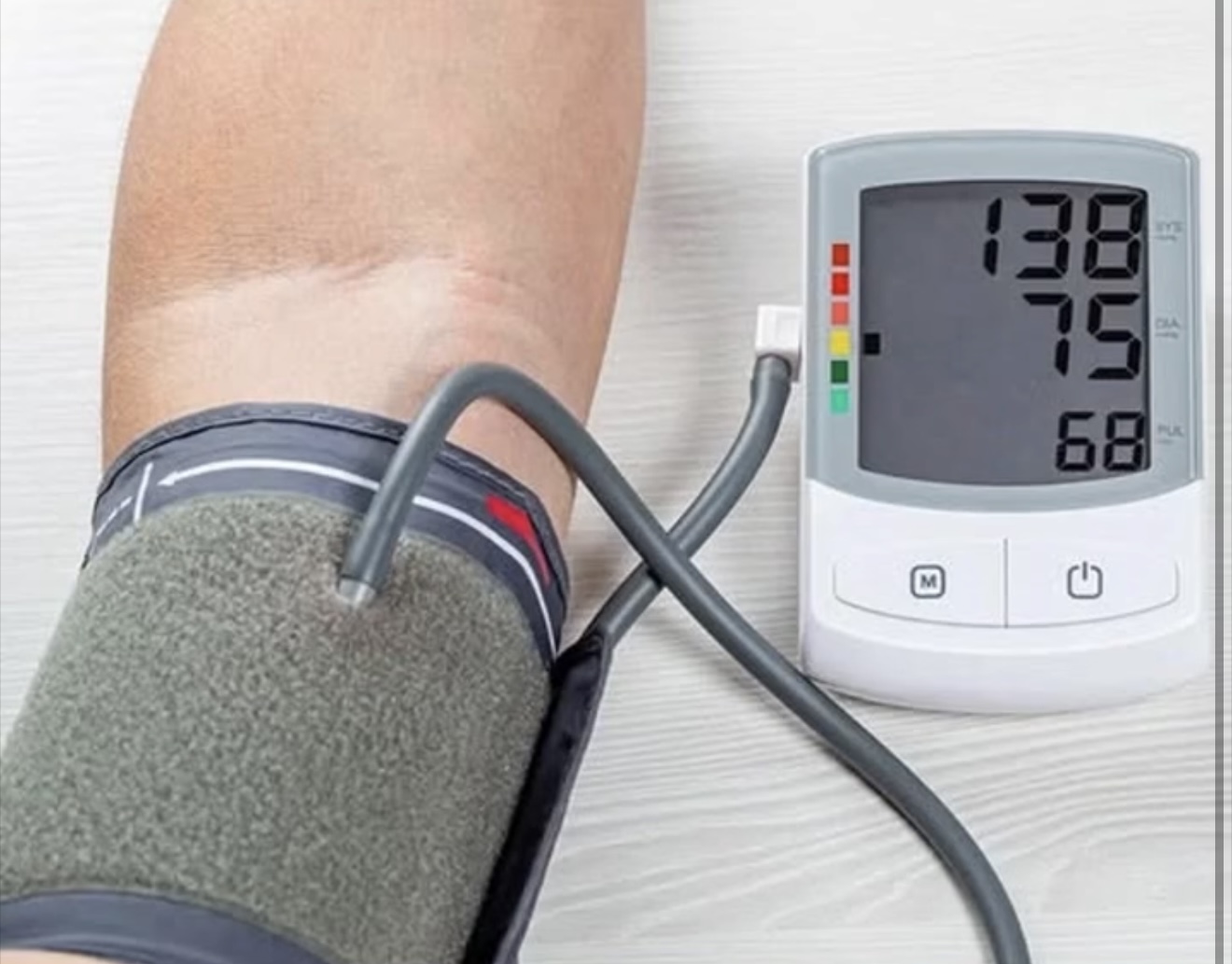
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against artery walls. A healthy reading is often around 120/80 mm Hg, but “normal” can vary with age and health. General adult ranges:
Low: under 90/60
Optimal: under 120/80
Normal: 120–129/80–84
High: above 140/90
Children’s levels increase gradually with age, while adult averages rise later in life. For example, women 18–39 average 110/68, while women 60+ average 139/68.
How Aging Affects Pressure
As you grow older, arteries stiffen and plaque builds up, making blood flow harder. Hormonal and kidney changes also play a role, raising the risk of hypertension—a leading factor in heart attacks, strokes, and dementia.
Staying Healthy at Any Age
The good news: lifestyle choices make a difference.
Maintain a healthy weight—even small losses help.
Eat smart—fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins (the DASH diet is recommended). Limit salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
Stay active—150 minutes of exercise weekly keeps vessels flexible.
Quit smoking—protects vessels immediately.
Limit alcohol—one drink daily for women, two for men.
Final Thought
High blood pressure may be common with age, but it’s not inevitable. Regular checks and small, consistent habits can keep your heart strong for years to come.